
Preventing the development of digital ulcers
Raynaud's phenomenon is a term which refers to colour changes (blue, white and red) occurring in the fingers and sometimes toes. Raynaud's syndrome usually occurs after exposure to cold temperatures.. It happens when blood flow to the hands, fingers or toes is temporarily reduced. Raynaud's can lead to swelling of the fingers, colour changes, numbness, pain, skin ulcers and gangrene in the fingers and toes. People with Raynaud's may have other diseases, and some people with Raynaud's may not have any other diseases.
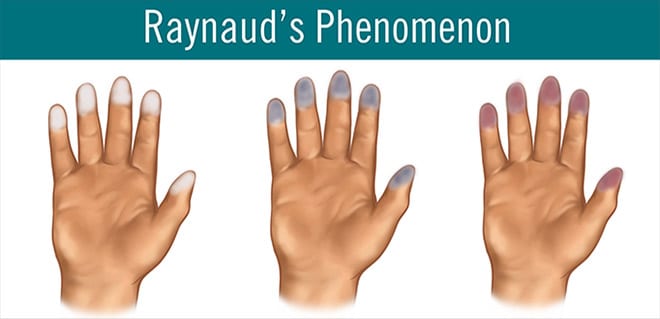
In patients diagnosed with scleroderma, Raynaud's phenomenon, digital ulcers and calcinosis are common manifestations. Digital ulcers occur in more than half of the patients.
Raynaud's phenomenon occurs in 2 main ways:
- The Primary Raynaud's is the most common form of the disorder and is not connected to an underlying disease or related medical problem.
- The Secondary Raynaud's is caused by for an underlying or related problem. Secondary Raynaud's is less common than the primary form, but tends to be a more severe disorder.
Symptoms of secondary Raynaud's often first appear at a later age - around 40 - while people with the primary form usually have symptoms earlier.
Causes of Raynaud's phenomenon
Blood vessels in the hands and feet seem to overreact to cold temperatures or stress.. When the body is exposed to cold temperatures, hands and feet can lose heat. The body slows down the blood supply to the fingers or toes to preserve core temperature.. And it specifically reduces blood flow by narrowing the small arteries under the skin of the fingers. In people with Raynaud's this normal response is exaggerated. Stress causes a similar reaction to cold
In Raynaud's, the arteries in the fingers go into a state called vasospasm. Vasospasm occurs when spasm of the blood vessel causes the blood vessels to constrict, critically and temporarily limiting the blood supply.
These same small arteries may thicken slightly, further limiting blood flow.. The affected skin turns a pale, dark colour due to the lack of blood flow to the area. Once the spasms disappear and blood returns to the area, the tissue may turn red before returning to normal skin colour.
Cold temperatures are more likely to trigger an attack. Exposure to cold can be as simple as putting your hands under cold running water, taking food out of the freezer or exposure to cold air. For some people, exposure to cold temperatures is not necessary. Emotional stress alone can cause a Raynaud's episode. Raynaud's may be partly an inherited disorder.
The causes of secondary Raynaud's include:
- Scleroderma
- Lupus
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Sjögren's syndrome
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Diseases of the arteries, such as atherosclerosis
- Injuries due to overuse
- Smoking
- Hand and foot injuries
- Certain medications, such as beta-blockers, which are used to treat high blood pressure; migraine medications containing ergotamine; medications containing estrogen; certain chemotherapy drugs; and medications that can narrow the blood vessels
- Chemical exposure: people exposed to vinyl chloride, such as those working in the plastics industry, may develop a disease similar to scleroderma. Raynaud's phenomenon may be part of this disease.
- Disorders of the thyroid gland
Treatment of Raynaud's phenomenon: hyperthermia
Prevention
Care and prevention measuressuch as wearing gloves or heavy socks, are generally effective in the treatment of mild Raynaud's symptoms.. If these are inadequate, drugs are available to treat more severe forms of the disease. The goals of treatment are:
- Reducing the number and severity of attacks
- Avoiding tissue damage
- Treat any underlying disease or condition

Medicines
Depending on the cause of the symptoms, medications may help treat Raynaud's syndrome. To widen (dilate) blood vessels and promote circulation, your doctor may prescribe:
- Calcium channel blockersThese drugs relax and open small blood vessels in the hands and feet. They lessen the frequency and severity of attacks in most people with Raynaud's. These drugs can also help heal skin ulcers on the fingers and toes.
- Alpha blockersSome people find relief with drugs called alpha blockers, which counteract the actions of norepinephrine, a hormone that constricts blood vessels.
- PDE-5 inhibitorsThese drugs can effectively relieve Raynaud's symptoms. These drugs include the high blood pressure medication losartan (Cozaar), the erectile dysfunction medication sildenafil (Viagra, Revatio), the antidepressant medication fluoxetine (Prozac, Sarafem) and a class of drugs called prostaglandins.
Surgeries and medical procedures
In cases of Severe Raynaud'sIf you have a history of a heart attack, medications may be inadequate, so your doctor may explore other treatment options:
- Nerve surgeryNerves called sympathetic nerves in your hands and feet control the opening and narrowing of blood vessels in your skin. In cases of severe Raynaud's, it may be necessary to cut these nerves to interrupt an exaggerated response. Through small incisions in the affected hands or feet, a doctor pulls away these tiny nerves around the blood vessels. Surgery, called sympathectomy, can reduce the frequency and duration of attacks, but is not always successful.
- Chemical injectionDoctors may inject chemicals to block the sympathetic nerves in the affected hands or feet. The procedure may need to be repeated if symptoms return or persist.
- AmputationSometimes, doctors need to remove tissue damaged by a lack of blood supply. This may include amputation of a Raynaud's toe or finger where the blood supply has been completely blocked and the tissue has developed gangrene. This surgery is very rarely used.
Hyperthermia
Hyperthermia, a heat radiation to raise the body temperature, with infrared-A with filtered water is a method that promotes rapid heat distribution in the body.while the epidermis is only slightly affected.

Hyperthermia has been shown to treat systemic scleroderma (AKT DERMATOL 1993) and to reduce Raynaud's phenomenon.
At Biosalud Day Hospital we have a total body hyperthermia bed for complementary treatments for cancer or chronic infections, which is unique in Spain.
We have long dealt with the autoimmune diseases of this type, in which the body produces an auto-attack response of the immune system against the body itself.

